Intubation
You have tearing and / or swelling of the inner corner of the eye, and / or superinfection of the tear ducts.
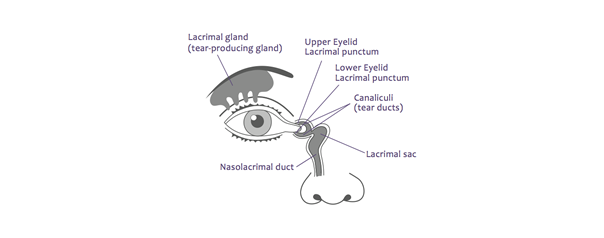
This may be due to an obstruction in the lacrimal passages.Intubation is defined by the placement in the tear drainage system of a tube to keep the canaliculus or the lacrimal-nasal duct open and remove the obstruction.
The indication for this procedure depends on the patient's age, the level of obstruction, the condition of the area, and the tear drainage system.
Your ophthalmologist suggests the operation because surgery is the only way to improve your condition. This sheet contains detailed information on the operation proposed to you, its results and its risks.
The intervention When there is an obstacle on the tear ducts or during chronic inflammation of these tear ducts, involves placing a silicone probe to keep the tear ducts open. These tear ducts have two canaliculi located at the level of the eyelids, a sac at the level of the inner corner of the eye and a duct which descends to the level of the nose (lacrimal-nasal duct).
Types of intubation
There are several types of intubation :
- - Bi-canaliculonasal intubation: which allows the passage of the probe through the two upper and lower canaliculi. Two strands of this silicone probe will be used, each passing through one of the two canaliculi. The two ends of the probes will be tied together and possibly fixed at the nose by a wire. A small loop of silicone will be visible in the inner corner of the eye, between the two tear points, upper and lower.
- - Mono-canaliculo-nasal intubation: which allows passage through a single palpebral canaliculus. A single strand of silicone will be placed in a canaliculus, mainly the lower one to the level of the nose. The wire will simply be cut at the nose. A small silicone collar will be visible at the edge of the eyelid that has been intubated.
Intubation is performed under general anesthesia. The intervention is relatively quick, lasting on average less than 5 minutes. A small amount of epistaxis can be seen during and a few hours after intubation, and will go away quickly. Placement of the catheter will help keep the tear ducts open. Due to the diameter of the probe tearing may persist after its placement. The shelf life of the probes varies from 4 to 6 months. The catheter is easily removed in the office without anesthesia.